7 Tips to Improve Your Organic Clickthrough Rate (CTR)
Gabriela Jhean
What Is Organic Clickthrough Rate?
Organic clickthrough rate (CTR) is the percentage of users who click on your listing in the search engine results page (SERP). It’s calculated by dividing the number of clicks by total impressions and multiplying by 100.
For example, if your search listing had 20 clicks and 100 impressions, your CTR would be 20%.
Table of Contents
Why Is Organic CTR Important?
A healthy organic CTR is critical for your online success. Without it, you risk a loss in SEO rankings and traffic, which can lead to missed opportunities to achieve your business goals.
Here are some of the key advantages of a strong organic CTR:
- Increased organic traffic: A higher CTR translates to more visitors to your website. This allows you to reach a wider audience, generate more leads, and boost conversions.
- Improved search engine rankings: Search engines consider user engagement metrics when ranking content. The recent Google algorithm leak also suggests that clicks are an important ranking signal. A high CTR shows search engines that users want to engage with your content, creating a positive feedback loop for higher rankings.
- Enhanced brand awareness: More clicks translate to more users seeing your website and brand. This increased visibility helps build brand awareness and establish authority in your industry.
Now, let’s see how you can increase your organic clickthrough rate.
7 Tips to Improve Your Organic Clickthrough Rate
1. Aim High on the SERP
Ranking on the first page of search engine results is vital for clicks.
And the higher you are — the better.
Ranking statistics reveal that the top 3 organic results receive 68.7% of all clicks.
So, how can you win these coveted spots?
It all starts with keyword research.
Keyword research is the backbone of an effective SEO strategy and creating content that ranks high in organic search results.
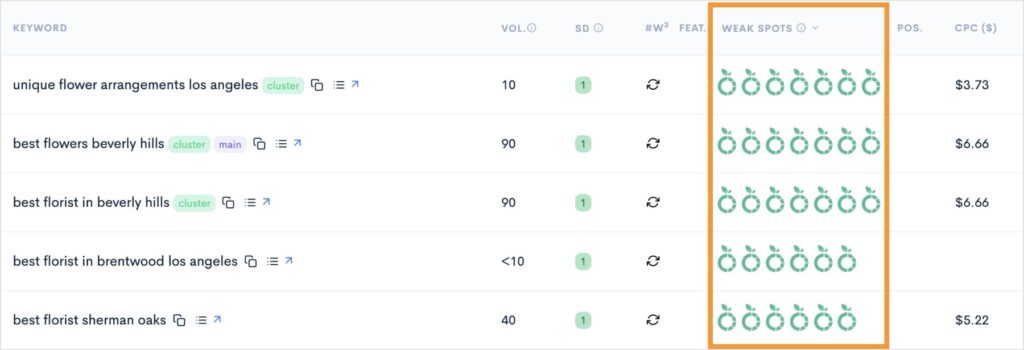
LowFruits can help you identify low-competition keywords that are easy to rank for. The KWFinder tool identifies weak domains ranking for your primary keyword, allowing you to discover the best keywords to target.
In the example below, the green icons represent the number of domains with weak authority ranking on the first page of Google. The more weak spots there are, the easier it is for you to outrank the competition and win one of the top positions.
2. Optimize for SERP Features
While it’s easy for website owners to fixate on high search rankings, they have little value if users don’t find your listing compelling enough to click.
That’s where SERP features come in.
SERP features are enhanced listings that display unique elements in search results.
There are several types, but here are just a few examples:
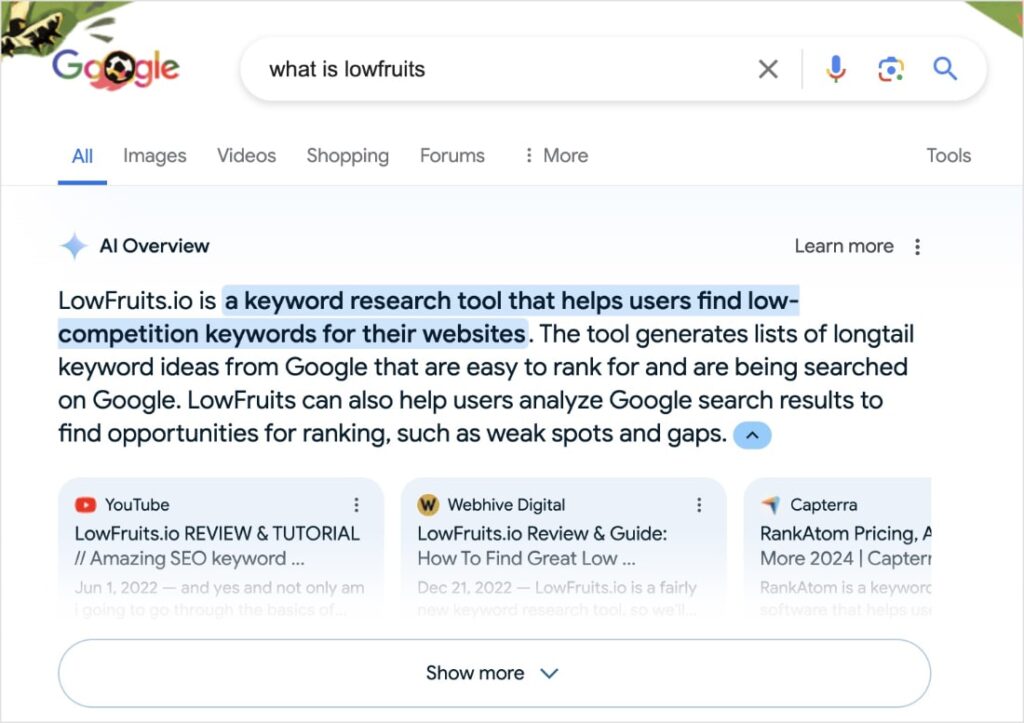
AI Overviews are Google’s newest SERP feature. They leverage artificial intelligence (AI) to generate summaries on the SERP.
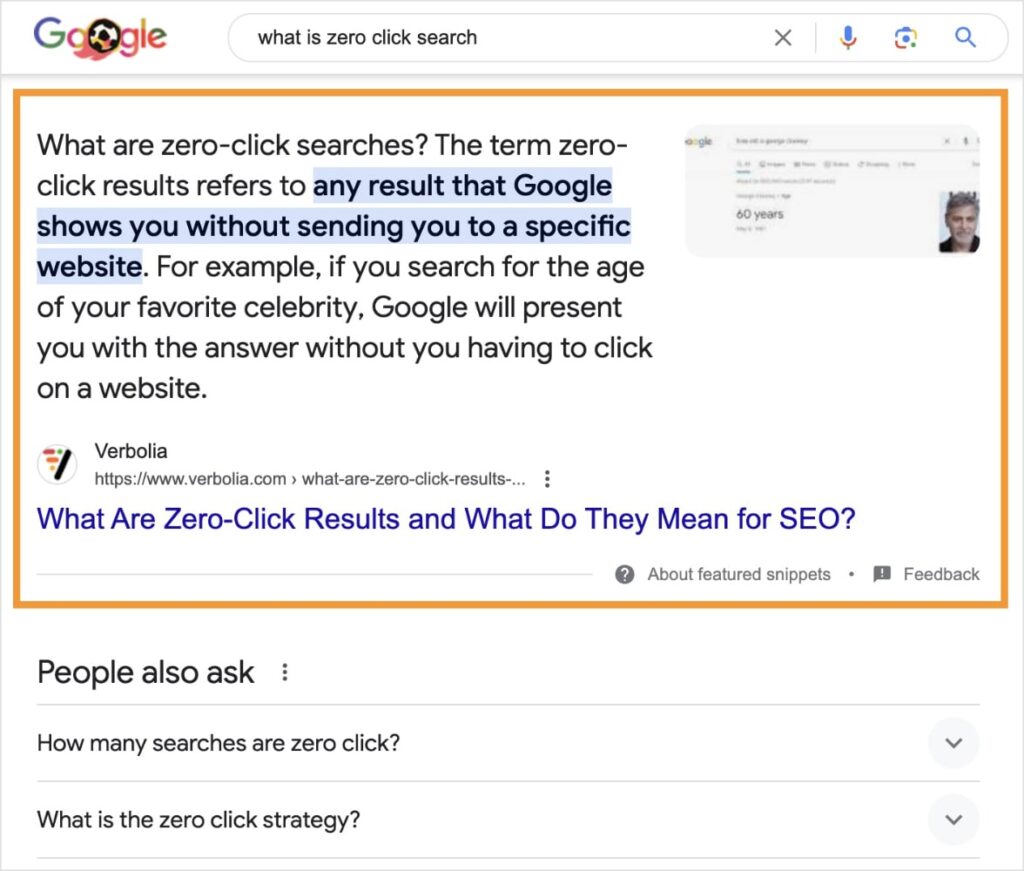
Featured snippets appear above all organic search listings. They answer the user’s query directly on the SERP.
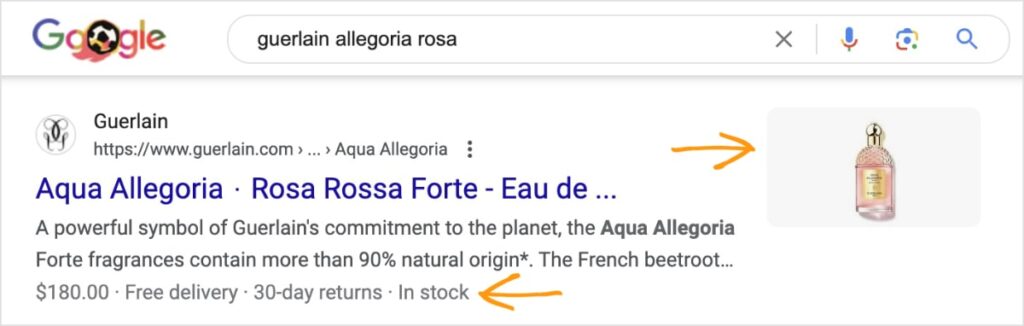
Rich snippets showcase additional elements, like product details, images, videos, etc. They’re eye-catching and can stop users from scrolling.
The People Also Ask (PAA) section shows users related questions to their search query. Users can expand these results to reveal the answer (and web page).
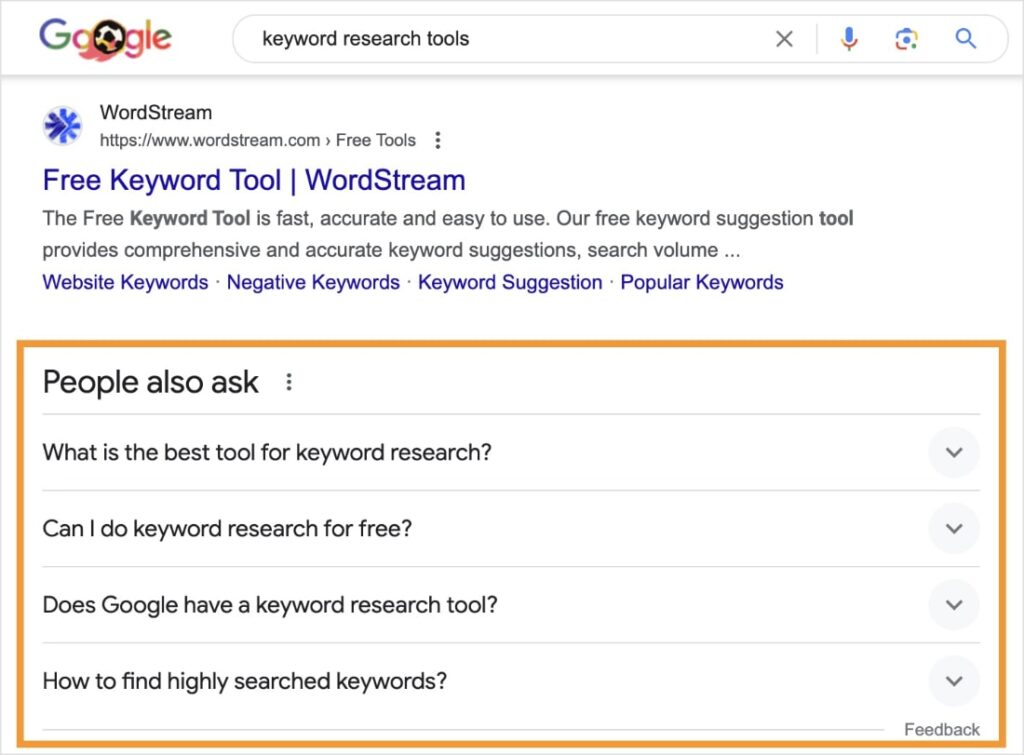
As you can see, SERP features are quite different from a standard “blue link” listing. They take up more space and provide a richer user experience.
SEO statistics also show that SERP features have high clickthrough rates.
Here’s a quick breakdown of some of the best-performing ones:
- Rich snippets get 58% of all clicks.
- Featured snippets have a CTR of 42.9%.
- Moving up from position 2 to position 1 generates 74.5% more clicks.
Alright, so we know that SERP features boost clickthrough rates, but how do you get them?
In addition to the basics (high-quality content, fulfilling search intent, positive user experience), there’s a technical SEO must-have to win this type of search result: schema markup.
Schema markup is a type of structured data that lives in your website’s HTML code. Search engines use this code to better understand your website and its content.
And the easier it is for search engines to understand your site, the easier it is for them to rank you.
If you’re adding schema markup to your site manually, you can use either of these tools:
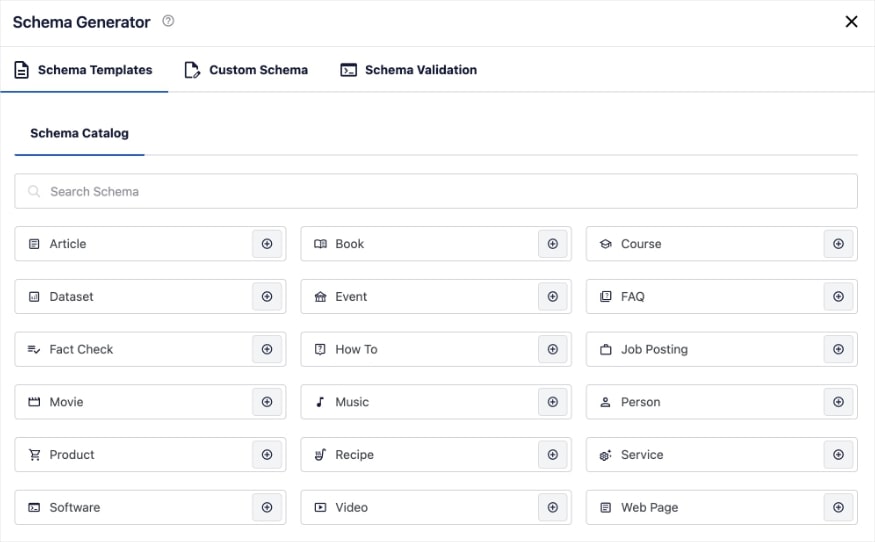
For WordPress users, All in One SEO (AIOSEO) has a Schema Generator that makes it super easy to add schema. No coding required.
Their rich snippets schema tool is as simple as picking your desired schema from a catalog. The plugin will automatically format the code for search engines.
Now, let’s look at another SERP feature that’s often overlooked: sitelinks.
3. Target Google Sitelinks
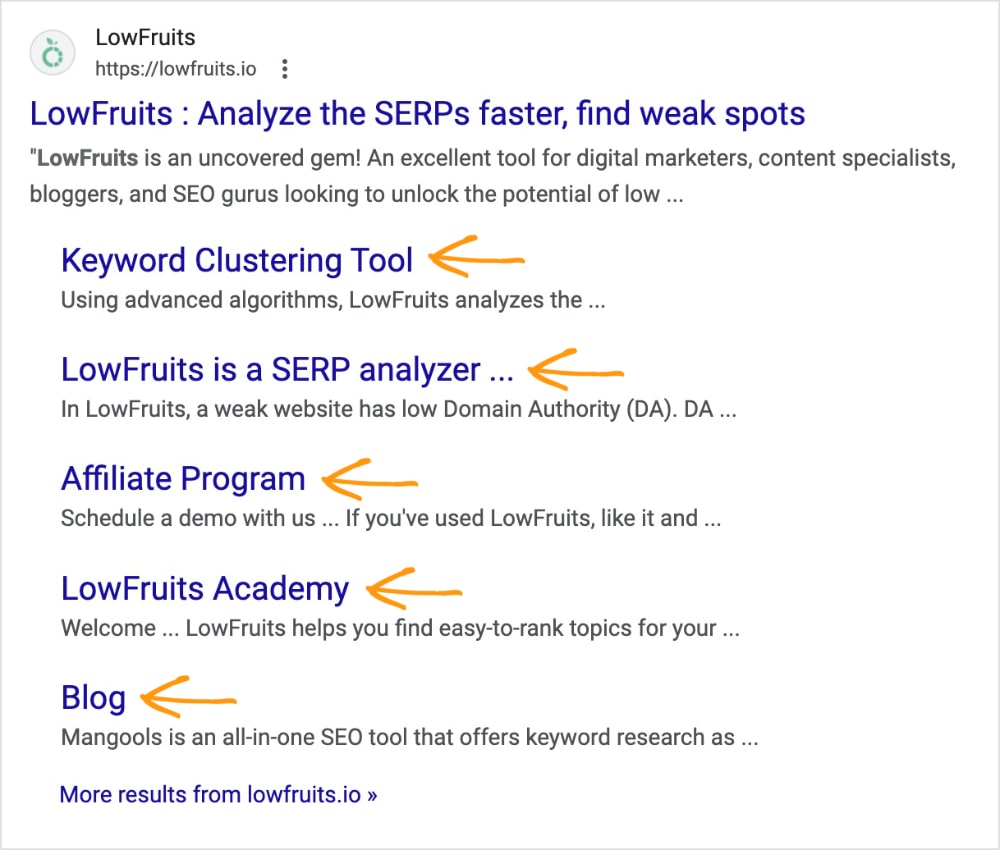
Sitelinks are additional links that appear below a search listing’s “main” link.
Homepages will often produce sitelinks that look like the example below. These links other entry points to the LowFruits website.
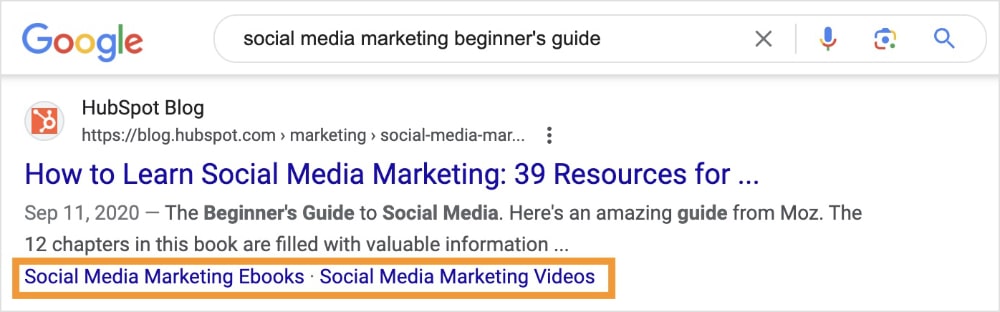
Search engines can also generate sitelinks for different areas of the same page.
In the example below, we see different sections of a HubSpot blog post. When a user clicks one of these links, they’ll jump to that section of the post.
Sitelinks are great for improving the content discoverability in organic search. They can introduce users to new areas of your site that may not have discovered otherwise.
As for how to get them, there are 2 key best practices:
- Create a logical structure for your content and use appropriate subheadings.
- Include a table of contents.
Sitelinks are generated on a per-search basis, so you can’t guarantee them. However, the actions above give you the best chance of generating this click-worthy search result.
4. Use the Right Keywords in the Right Places
As we saw in our first tip to improve your CTR, keywords are the foundation for any successful SEO strategy. They serve as the bridge between users’ queries and your content.
But identifying the right keywords is only the first step.
Now, you have to put them in the right places.
Your primary keyword should appear in the following areas to grab users’ attention on the SERP:
- Page title
- Meta description
- URL
Placing keywords in these areas can help users recognize that your content aligns with their search intent as they scan listings. This can increase your CTR and, ultimately, drive more organic traffic to your site.
Now, let’s take a closer at what search intent means.
5. Decipher Search Intent
Search intent is the why behind someone’s search. It’s what motivates a user to perform a search.
Understanding and catering to search intent is a critical aspect of optimizing your organic CTR.
It can be broadly categorized into 4 main types:
- Informational: Users seek to acquire knowledge or gather information about a particular topic.
- Navigational: Users aim to locate a specific website or webpage.
- Commercial: Users are researching products or services with the intention of making a purchase in the near future.
- Transactional: Users are ready to take immediate action, such as making a purchase or completing a transaction.
To decipher a keyword’s search intent, you’ll need to perform a SERP analysis.
A SERP analysis is the process of analyzing the top-ranking results for a specific keyword. By studying what pages search engines serve for that keyword, you can align your content with the search intent.
LowFruits makes this process easy.
When you’re looking at a keyword report, you can View the SERP directly from the tool.
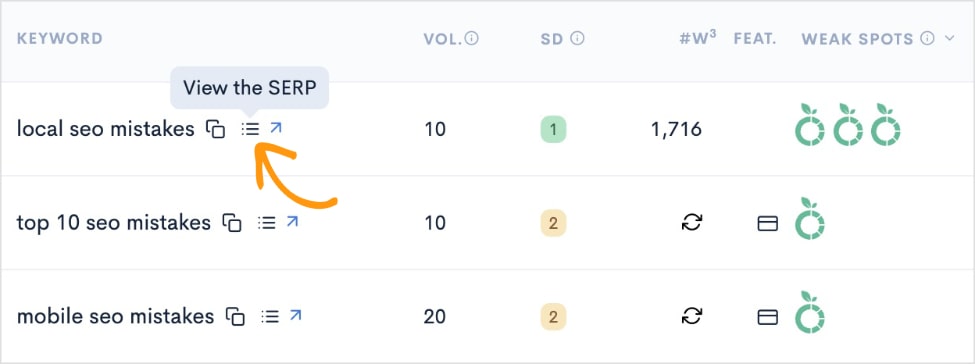
Clicking this button will open a pop-out view of the top 10 organic results for your keyword.
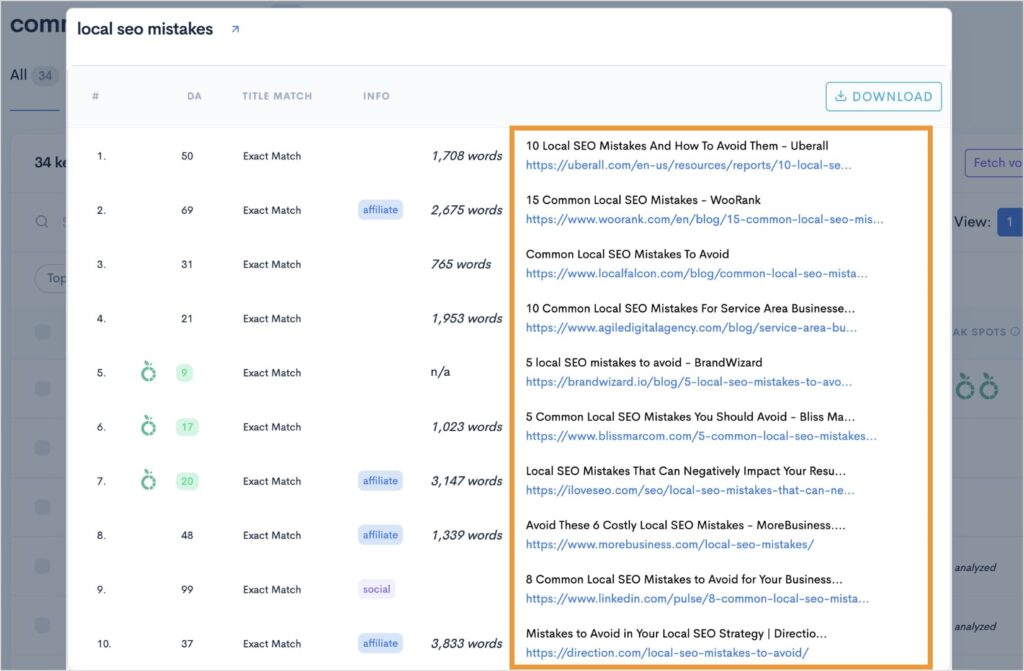
You can then see how competitors optimize their page titles and URLs (2 key components of our previous strategy). You can also click any of these links to open the page and see how they’re addressing the subject.
Mastering the art of deciphering search intent is a core SEO best practice. It enhances the overall content creation process and user experience, which can ultimately boost your CTR.
6. Write Click-worthy Metadata
Crafting compelling metadata for your web pages is vital to getting more organic clicks.
Your meta title, also called page title or SEO title, and meta description serve as a digital billboard, enticing users to click.
Here are key strategies for creating click-worthy metadata:
- Use action-oriented language. Encourage action with dynamic verbs like “discover,” “unlock,” or “learn.” This creates urgency and appeals to potential visitors.
- Stay within length limits. Keep meta titles between 50-60 characters and descriptions within 150-160 characters. This ensures your message isn’t cut off in search results.
- Incorporate your target keywords. Include relevant keywords naturally to enhance SEO and catch users’ eyes. Avoid keyword stuffing, which can deter clicks.
- Highlight unique selling points (USPs). Differentiate your content by emphasizing unique benefits, such as “exclusive tips” or “comprehensive guide,” to attract clicks.
- Leverage emotional triggers. Appeal to users’ emotions with phrases like “don’t miss out” or “essential tips” to motivate clicks through emotional connection. Time-sensitive triggers are particularly effective for boosting sales, too.
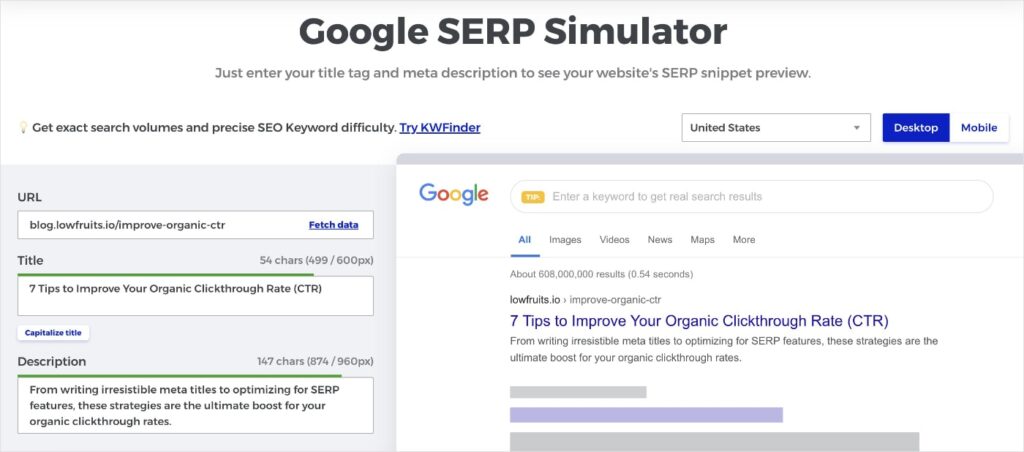
I like to write my metadata directly in a SERP preview tool. This allows me to play with different variations, see how they look on the SERP, and pick the one I think will perform best.
Mangools has a free SERP simulator, which is my go-to tool.
Here’s an example of what it looks like for this article:
If I’m working in WordPress, I also love AIOSEO’s SERP preview feature. It shows you a search listing preview directly in the WordPress editor. It’s convenient because you don’t have to jump out to another tool.
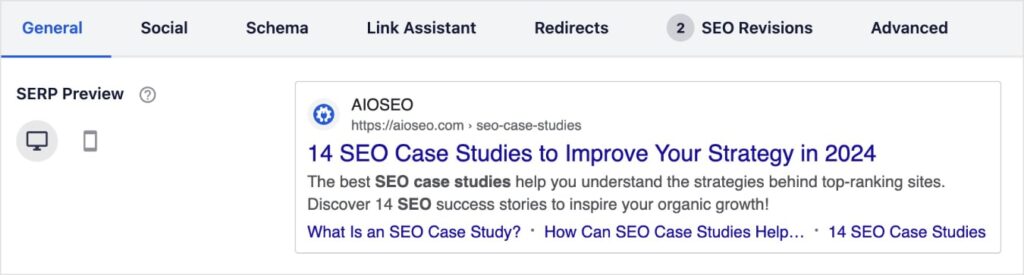
(Notice those sitelinks we talked about earlier, too? I like how AIOSEO shows these in the preview, making it more robust than Mangools.)
7. Make URLs SEO-Friendly
URLs are easy to overlook for busy business owners who are running their own websites.
But they’re a vital component of your SEO efforts, and they’re super easy to optimize.
With URLs, the simpler, the better.
Here’s how to optimize your URLs for more clicks:
- Keep URLs short and descriptive.
- Include your primary keyword.
- Use hyphens (-), not underscores (_).
- Use lowercase letters.
- Don’t use special characters.
- Make sure they’re easy to read.
- Reflect your site structure.
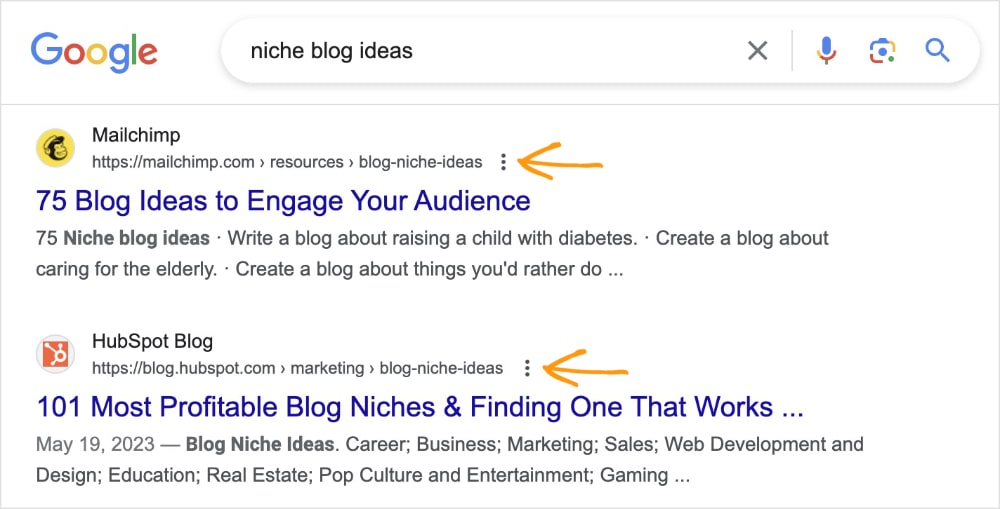
The examples below reflect these URL best practices. (They have strong meta titles, too.)
Organic Clickthrough Rate FAQs
1. What is a good CTR for organic search?
A good organic CTR varies greatly by ranking position. For example, the first organic result on page 1 of the SERP has an average CTR of 39.8%, whereas a listing in position 8 has a 2.1% CTR. That’s why it’s important to consider your site’s position when trying to determine if you have a “good” CTR.
2. What’s considered a low CTR?
A low CTR would be anything below the average CTR for that ranking position. You can reference CTR benchmarks to determine what that percentage should be. (AIOSEO has a helpful chart that breaks down CTR by ranking position.)
3. Is CTR a ranking factor?
Google hasn’t confirmed clickthrough rate as a ranking factor. However, it does show how users interact with your content, which could influence Google rankings. The recent algorithm leak supports this theory, suggesting that clicks are a ranking signal.
4. How do I calculate organic CTR?
You can use the following formula to calculate your organic clickthrough rate: Organic CTR = (Number of Clicks) / (Number of Impressions) x 100
Final Thoughts
Now that you know how to improve your organic clickthrough rate, it’s time to put these strategies into action.
Remember, a healthy CTR is crucial for your online success.
And there’s no time like the present to start making the optimizations you want to increase your CTR, grow your organic traffic, and achieve your business goals.
Here’s further reading to help you get the most out of your SEO: